👋 About Me
Hi, I am currently pursuing a PhD at the State Key Laboratory of Multimodal Artificial Intelligence System, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CASIA), under the guidance of Prof. Weiming Hu, Prof. Bing Li, Prof. Chunfeng Yuan and Associate Prof. Juan Wang.
Before that, I got my bachelor’s degree from Beijing Jiaotong University (BJTU) in 2022. Especially thank Prof. Runming Cong and Prof. Fangshi Wang for their guidance during this period.
I'd like to solve practical challenges motivated by real-world industrial problems, and have published some papers at the top international venues (ECCV, CVPR, IJCV, etc.) 
💡My research interests include:
Computational Imaging
- Image Quality Assessment (IQA)
- AI Image Signal Processing (AI-ISP)
- 3A Algorithms
Multimodal Understanding
- Vision-Language Models (VLM)
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Recently, my research focuses on developing a unified foundational model for IQA that can support multiple IQA tasks, such as quality prediction and distortion localization. In parallel, I am also working on an AI-driven pet companion project 🐾 that helps pet owners curate warm, lasting memories and better meet their genuine companionship needs. I would be pleased to connect with anyone who shares interests in these directions.
📫 My email: chencn2018@163.com, chenzewen2022@ia.ac.cn
🏁 Repositories
🔥 News
- Our IQA solution has been deployed at OPPO in practical production. It transforms assessment from a subjective process into an objective one and reduces the evaluation workload from approximately two person-days to 0.1 person-days.
- We were invited to give a talk at Apple Inc. .
- Our work Visual-Instructed Degradation Diffusion for All-in-One Image Restoration was accepted by The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2025 (CVPR 2025).
- We were invited to give a talk at DJI Inc.
- Our work MobileIQA: Exploiting Mobile-level Diverse Opinion Network For No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Using Knowledge Distillation was accepted by The 18th European Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ECCVW 2024).
- Our work PromptIQA: Boosting the Performance and Generalization for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment via Prompts was accepted by The 18th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV 2024).
- We won the second prize in the "AIGC Inference Performance Optimisation Track" held by Baidu.
- Our work Hierarchical Curriculum Learning for No-reference Image Quality Assessment was accepted by International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV).
- Our work Teacher-Guided Learning for Blind Image Quality Assessment was accepted by The 16th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV 2022).
📝 Publications

Zewen Chen, Juan Wang, Bing Li, et al.
TL;DR: We introduce a prompt-driven no-reference IQA framework that adapts to diverse, unseen assessment requirements by encoding ARs from a few image-score exemplar prompts. To prevent shortcut learning, we train with hybrid AR augmentation (monotonic relabeling + Gaussian latent AR sampling), yielding AR-consistent predictions.
Quick Read (Click Me)
Coming Soon.
Wenyang Luo, Haina Qin, Zewen Chen, Libin Wang, et al. (Co-first author)
TL;DR: We propose Defusion, an all-in-one image restoration framework that uses visual instruction-guided degradation diffusion to handle diverse and mixed degradations with a single, generalizable model.
Quick Read (Click Me)
Image restoration tasks like deblurring, denoising, and dehazing usually need distinct models for each degradation type, restricting their generalization in real-world scenarios with mixed or unknown degradations. In this work, we propose Defusion, a novel all-in-one image restoration framework that utilizes visual instruction-guided degradation diffusion. Unlike existing methods that rely on taskspecific models or ambiguous text-based priors, Defusion constructs explicit visual instructions that align with the visual degradation patterns. These instructions are grounded by applying degradations to standardized visual elements, capturing intrinsic degradation features while agnostic to image semantics. Defusion then uses these visual instructions to guide a diffusion-based model that operates directly in the degradation space, where it reconstructs highquality images by denoising the degradation effects with enhanced stability and generalizability. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that Defusion outperforms state-ofthe-art methods across diverse image restoration tasks, including complex and real-world degradations.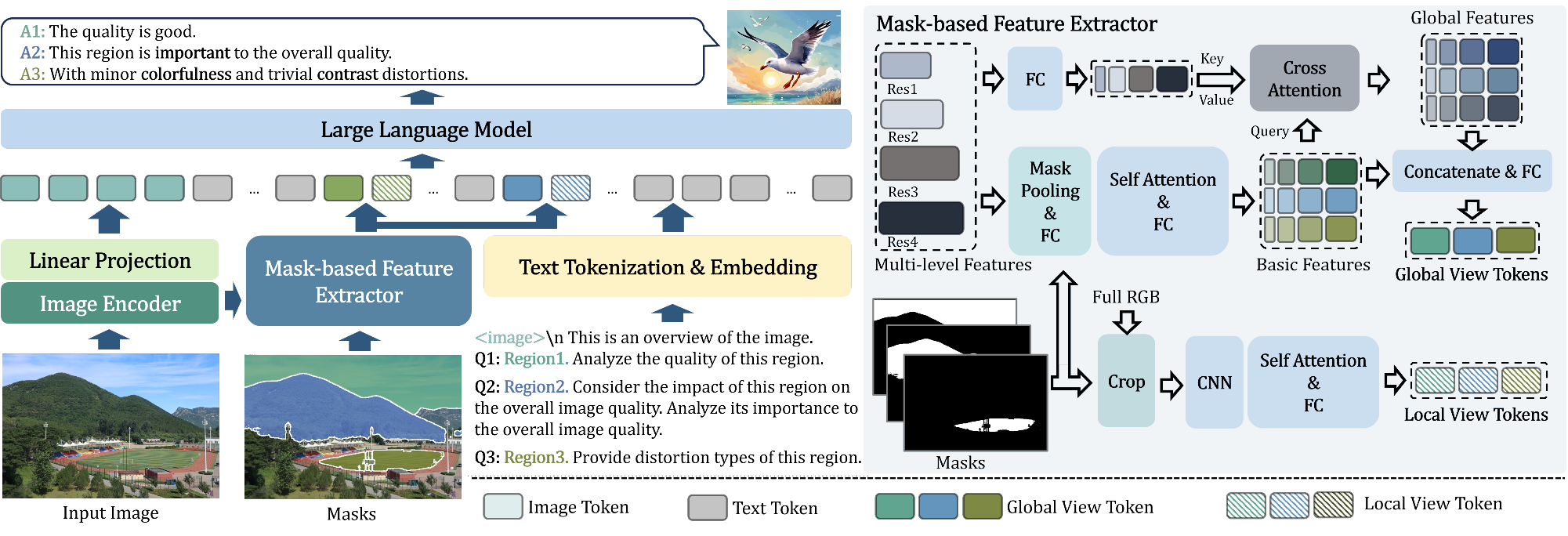
Zewen Chen, Juan Wang, Wen Wang, Sunhan Xu, et al.
TL;DR: We propose a novel network (SEAGULL) and construct two datasets (SEAGULL-100w and SEAGULL-3k) to achieve fine-grained IQA for any ROIs.
Quick Read (Click Me)
Existing Image Quality Assessment (IQA) methods achieve remarkable success in analyzing quality for overall image, but few works explore quality analysis for Regions of Interest (ROIs). The quality analysis of ROIs can provide fine-grained guidance for image quality improvement and is crucial for scenarios focusing on region-level quality. This paper proposes a novel network, SEAGULL, which can SEe and Assess ROIs quality with GUidance from a Large vision-Language model. SEAGULL incorporates a vision-language model (VLM), masks generated by Segment Anything Model (SAM) to specify ROIs, and a meticulously designed Mask-based Feature Extractor (MFE) to extract global and local tokens for specified ROIs, enabling accurate fine-grained IQA for ROIs. Moreover, this paper constructs two ROI-based IQA datasets, SEAGULL-100w and SEAGULL-3k, for training and evaluating ROI-based IQA. SEAGULL-100w comprises about 100w synthetic distortion images with 33 million ROIs for pre-training to improve the model's ability of regional quality perception, and SEAGULL-3k contains about 3k authentic distortion ROIs to enhance the model's ability to perceive real world distortions. After pre-training on SEAGULL-100w and fine-tuning on SEAGULL-3k, SEAGULL shows remarkable performance on fine-grained ROI quality assessment.
Quick Read (Click Me)
With the rising demand for high-resolution (HR) images, No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (NR-IQA) gains more attention, as it can ecaluate image quality in real-time on mobile devices and enhance user experience. However, existing NR-IQA methods often resize or crop the HR images into small resolution, which leads to a loss of important details. And most of them are of high computational complexity, which hinders their application on mobile devices due to limited computational resources. To address these challenges, we propose MobileIQA, a novel approach that utilizes lightweight backbones to efficiently assess image quality while preserving image details through high-resolution input. MobileIQA employs the proposed multi-view attention learning (MAL) module to capture diverse opinions, simulating subjective opinions provided by different annotators during the dataset annotation process. The model uses a teacher model to guide the learning of a student model through knowledge distillation. This method significantly reduces computational complexity while maintaining high performance. Experiments demonstrate that MobileIQA outperforms novel IQA methods on evaluation metrics and computational efficiency.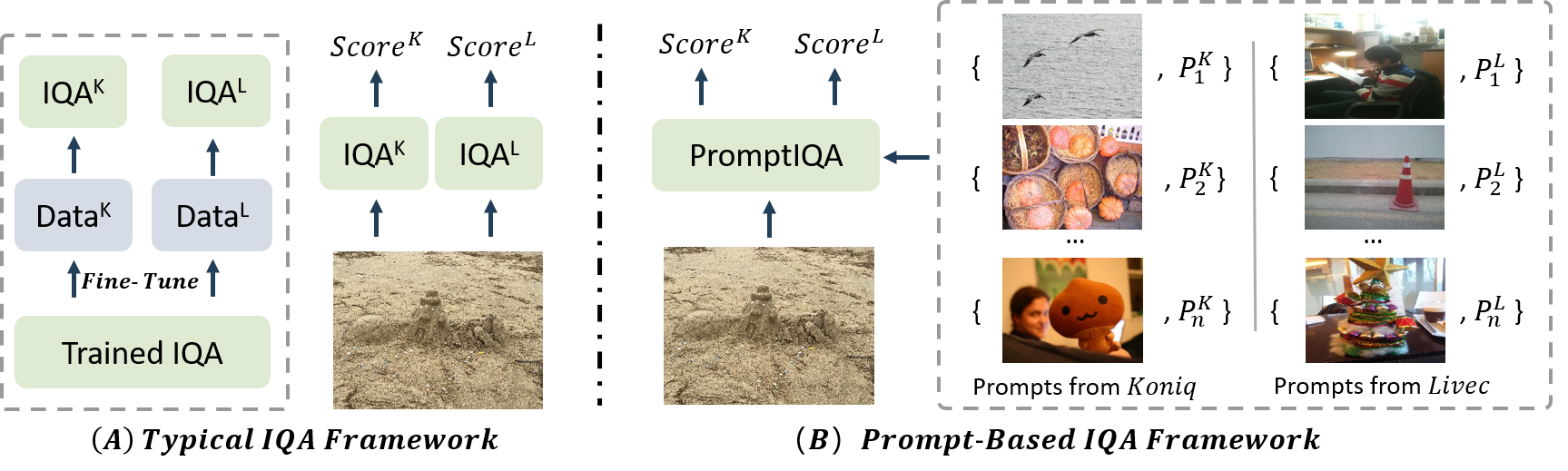
Quick Read (Click Me)
Due to the diversity of assessment requirements in various application scenarios for the IQA task, existing IQA methods struggle to directly adapt to these varied requirements after training. Thus, when facing new requirements, a typical approach is fine-tuning these models on datasets specifically created for those requirements. However, it is time-consuming to establish IQA datasets. In this work, we propose a Prompt-based IQA (PromptIQA) that can directly adapt to new requirements without fine-tuning after training. On one hand, it utilizes a short sequence of Image-Score Pairs (ISP) as prompts for targeted predictions, which significantly reduces the dependency on the data requirements. On the other hand, PromptIQA is trained on a mixed dataset with two proposed data augmentation strategies to learn diverse requirements, thus enabling it to effectively adapt to new requirements. Experiments indicate that the PromptIQA outperforms SOTA methods with higher performance and better generalization.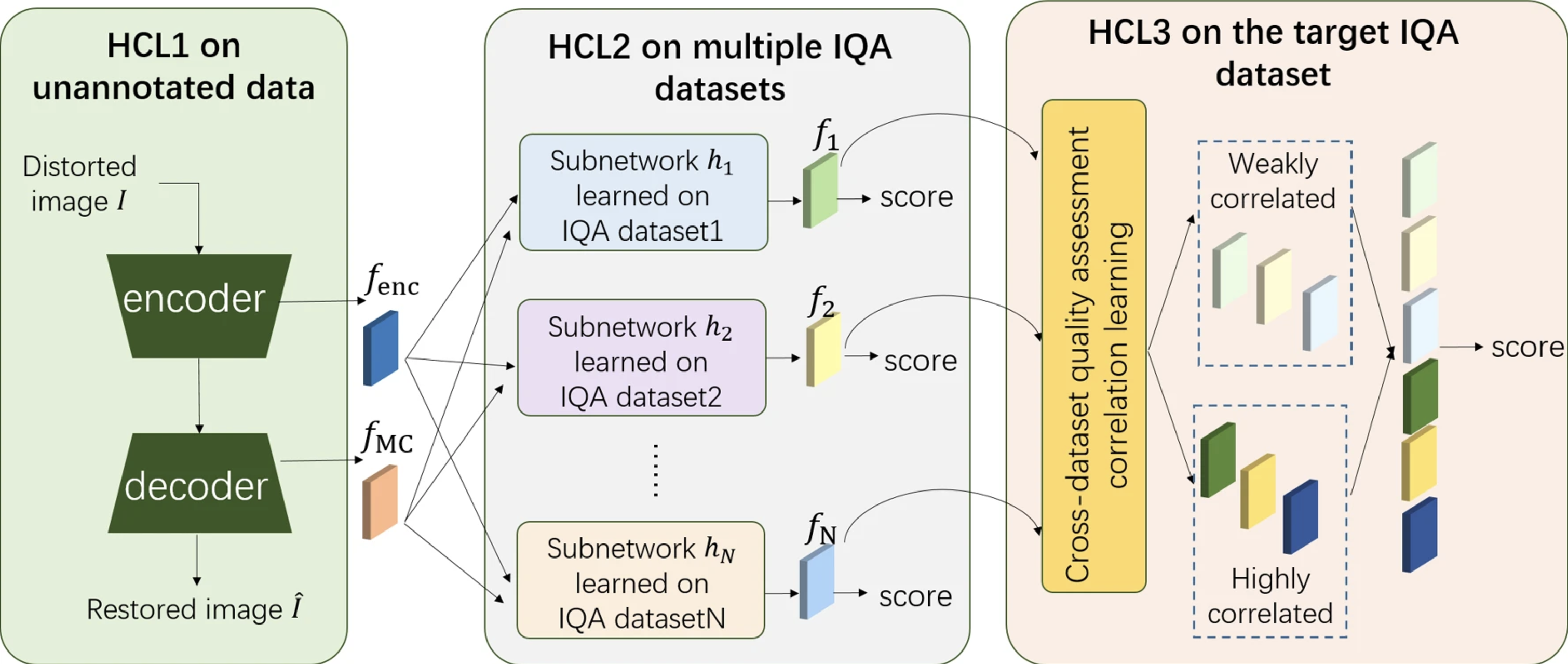
Juan Wang, Zewen Chen, Chunfeng Yuan et al. (Co-first author)
TL;DR: We develope a hierarchical curriculum learning (HCL) framework for NR-IQA by decomposing complex tasks into three levels: basic, intermediate, and professional to improve performance.
Quick Read (Click Me)
This work addresses the problem of insufficient labeled data for no-reference image quality assessment (NR-IQA) with the help of pre-training techniques and external unsupervised data. We design a hierarchical curriculum learning (HCL) framework for NR-IQA, which leverages the external data to learn the prior knowledge about IQA widely and progressively. Specifically, as a closely-related task with NR-IQA, image restoration is used as the first curriculum to learn the image quality related knowledge (i.e., semantic and distortion information) on massive distorted-reference image pairs. Then multiple lightweight subnetworks are designed to learn human scoring rules on multiple available synthetic IQA datasets independently, and a cross-dataset quality assessment correlation (CQAC) module is proposed to fully explore the similarities and diversities of different scoring rules. Finally, the whole model is fine-tuned on the target authentic IQA dataset to fuse the learned knowledge and adapt to the target data distribution. The experimental results show that the designed pre-trained model can achieve good prediction accuracy and generalisation.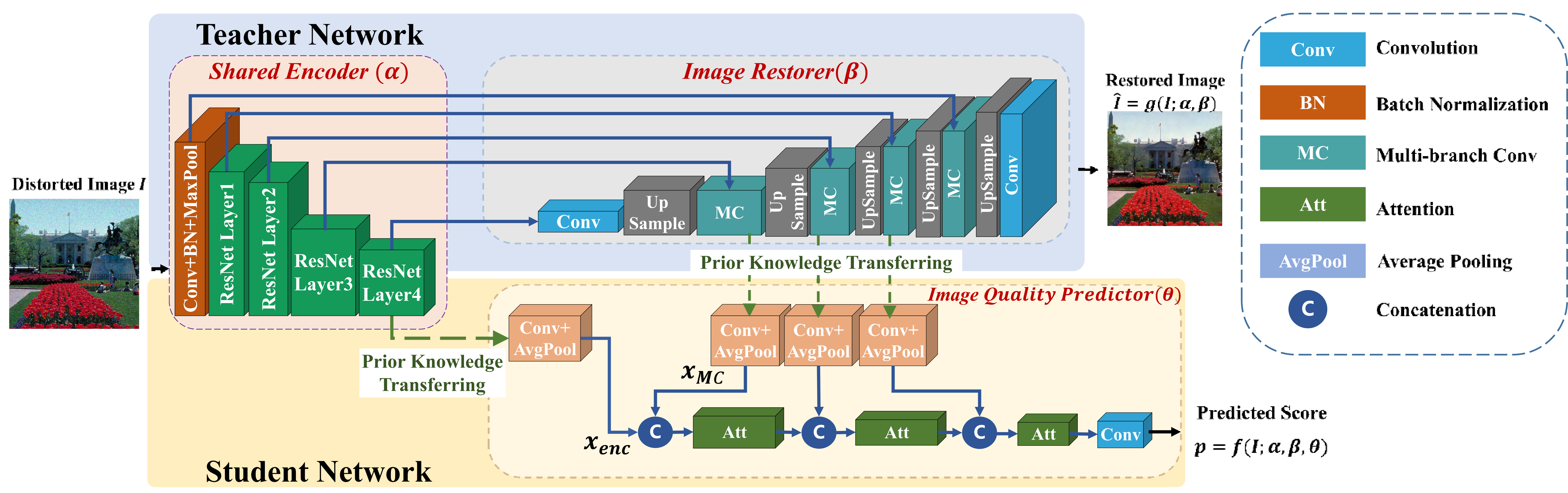
Zewen Chen, Juan Wang, Bing Li et al.
TL;DR: We introduce a novel NR-IQA framework that leverages an image restoration teacher network (TN) to transfer semantic and distortion knowledge to a student network (SN), enabling superior BIQA performance on limited annotated data with validated generalization, robustness, and effectiveness.
Quick Read (Click Me)
The performance of deep learning models for blind image quality assessment (BIQA) suffers from annotated data insufficiency. However, image restoration, as a closely-related task with BIQA, can easily acquire training data without annotation. Moreover, both image semantic and distortion information are vital knowledge for the two tasks to predict and improve image quality. Inspired by these, this paper proposes a novel BIQA framework, which builds an image restoration model as a teacher network (TN) to learn the two aspects of knowledge and then guides the student network (SN) for BIQA. In TN, multi-branch convolutions are leveraged for performing adaptive restoration from diversely distorted images to strengthen the knowledge learning. Then the knowledge is transferred to the SN and progressively aggregated by computing long-distance responses to improve BIQA on small annotated data. Experimental results show that our method outperforms many state-of-the-arts on both synthetic and authentic datasets. Besides, the generalization, robustness and effectiveness of our method are fully validated.🏆 Projects
-
12/2024-01/2026: Image Representation Factor Prediction and Artifact Analysis
What I do: Propose effective solutions for ghosting and flicker artifact detection, as well as methods for detecting and assessing video stabilization performance.
Output: Deployed in practical production.Some Visualizations (Click Me)
Coming Soon. -
06/2021-10/2024: AI-Based Black Box ISP Hyperparameter Optimization
What I do: The development of NR-IQA, the identification and evaluation of scene factors and artifacts.
Output: ECCV2024, IJCV and ACCV2022
- 12/2024-Now: TBU
🎖 Honors and Awards
- 08/2023: The second prize in the “AIGC Inference Performance Optimisation Track” held by Baidu.
📖 Educations
- 2022.09 - Now PhD: State Key Laboratory of Multimodal Artificial Intelligence System, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CASIA)
- 2018.09 - 2022.06 Bachelor: School of Software, Beijing Jiaotong University (BJTU)

















